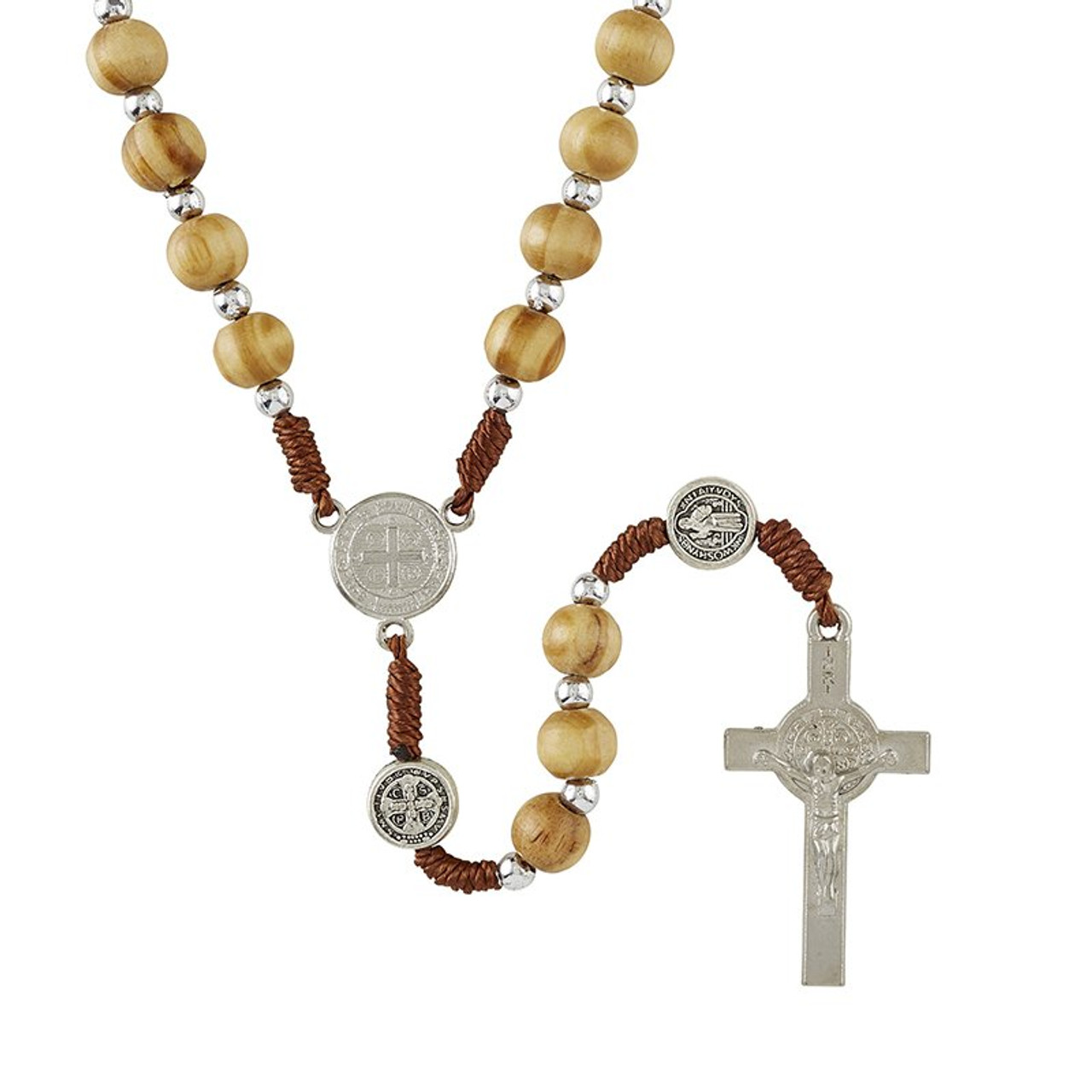

St. Benedict, also known as Saint Benedict of Nursia, was an Italian Christian monk, writer, and theologian. He lived during the late 5th and early 6th centuries. Here are some key points about his life and influence:
-
Founder of the Benedictine Monastery: St. Benedict established the Benedictine monastery at Monte Cassino in Italy. This monastery became a significant center for monastic life and learning.
-
Father of Western Monasticism: His Rule, known as the Benedictine Rule, became the standard for monastic living across Europe. It emphasized prayer, work, and community life. Monks following this rule contributed to the evangelization and civilization of many European countries during the Middle Ages.
-
Patron Saint of Europe: In recognition of the impact of Benedictine monks, Pope Paul VI declared St. Benedict the patron saint of all Europe in 1964.
-
Historical Context: Benedict’s life spanned a period of transition from the decayed Roman Empire to the medieval papacy. He served as a link between Eastern monasticism and the emerging new age.
-
Retreat to Solitude: Shocked by the licentiousness of Rome, Benedict retired to a cave near Subiaco, where he lived a life of prayer and asceticism.
-
Feast Day: St. Benedict’s feast day is celebrated on July 11 (formerly March 21).

Recent Comments